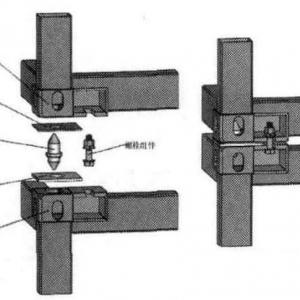
Steel structure processing
The following is a full analysis of welding H-shaped steel, box-shaped columns, lattice columns, and cross columns to understand the production process of steel structure processing, key details to pay attention to, and main application scenarios.1. Processing process and precautions for welding H-shaped steel
1. Cutting: Cut the steel into the required length and width according to the design requirements. In this link, the accuracy of the cutting size must be ensured, and the error should be controlled within a very small range.
2. Assembly: Assemble the cut flange plate and web plate to form the shape of the H-shaped steel. During the assembly process, the verticality of the flange plate and the web plate, as well as the dimensional accuracy of each part, must be ensured.
3. Welding: Use welding methods such as automatic submerged arc welding to weld the assembled H-shaped steel. When welding, pay attention to the reasonable setting of parameters such as welding current, voltage, and speed to ensure the quality of the weld. At the same time, the weld should be inspected to ensure the firmness and sealing of the welding.
4. Correction: The H-shaped steel after welding may be deformed and needs to be corrected. Correction can be done by mechanical correction or flame correction to make the size and shape of the H-shaped steel meet the design requirements.
Pay attention to details:
- The selection of welding materials must meet the design requirements to ensure welding strength.
- During welding, pay attention to prevent welding defects such as pores, slag inclusions, cracks, etc.
- During correction, the correction force must be controlled to avoid excessive correction that may cause damage to the steel.
2. Box column processing process and precautions
1. Cutting: Cut the steel plate into the required size as the four panels of the box column.
2. Beveling: Beveling the edges of the panels so that they can be better fused during welding.
3. Assembly: Assemble the four panels into the shape of a box column, and install internal partitions and other strengthening structures. During the assembly process, ensure the verticality and dimensional accuracy of each panel, as well as the accurate position of the internal structure.
4. Welding: Weld the four welds of the box column. The welding method usually uses submerged arc welding or gas shielded welding. During welding, attention should be paid to the control of welding sequence and welding parameters to reduce welding deformation.
5. Correction: Correct the box column after welding so that its size and shape meet the design requirements.
Pay attention to details:
- The welding quality of the internal partition is very important. Ensure that the welding is firm to avoid problems during use.
- Reasonable arrangement of welding sequence can effectively reduce welding deformation and improve the processing quality of box columns.
- The dimensional accuracy requirements of box columns are high, and multiple measurements and adjustments are required during the processing.
III. Lattice column processing process and precautions
1. Make limbs: Process steel into limbs of lattice columns, usually angle steel or channel steel.
2. Assembly: Assemble the limbs according to the design requirements to form the frame structure of the lattice column. During the assembly process, the position and verticality of the limbs must be ensured.
3. Welding: Weld the connection parts of the limbs to ensure the overall stability of the lattice column. Pay attention to welding quality and welding strength during welding.
4. Installation of gussets: Install gussets between the limbs of the lattice column to enhance the rigidity and stability of the lattice column. The installation of gussets should be firm and reliable, and the spacing should meet the design requirements.
Pay attention to details:
- The processing accuracy of the limbs directly affects the quality of the lattice column, and the size and angle of the limbs should be strictly controlled.
- Pay attention to the selection of welding process during welding to ensure welding quality.
- The installation of gussets should be evenly distributed to ensure that the lattice column is evenly stressed.
IV. Processing process and precautions of cross columns
1. Cutting: Cut the steel plate into various parts of the cross column, including the web, flange plate, etc.
2. Assembly: Assemble the web and flange plates to form the shape of a cross column. During the assembly process, the verticality and dimensional accuracy of each component must be ensured.
3. Welding: Weld the welds of the cross column. The welding method usually adopts gas shielded welding or submerged arc welding. When welding, pay attention to the control of welding sequence and welding parameters to reduce welding deformation.
4. Correction: Correct the cross column after welding so that its size and shape meet the design requirements.
Pay attention to details:
- The welding of the cross column is difficult, so it is necessary to choose the appropriate welding process and welding materials.
- During the welding process, attention should be paid to prevent welding defects, such as lack of fusion and lack of penetration.
- When correcting, appropriate methods should be used to avoid damage to the structure of the cross column.
V. Main application scenarios
1. Welding H-shaped steel
Welding H-shaped steel has the advantages of strong bending resistance, simple construction and relatively low cost. It is widely used in the following scenarios:
1. Industrial plant: It is a common component for the construction of various Steel structure workshops. It can be used to support the roof and wall structure of the plant and bear large roof loads and crane loads.
2. Multi-story building frame: In the frame steel structure of multi-story buildings, H-shaped steel can be used as beams and columns to provide stable structural support for the building.
3. Bridge engineering: It can be used for bridge steel structures of small and medium span bridges to bear the loads of vehicles and pedestrians.
2. Box-type columns
Box-type columns have good compression, bending and torsion resistance, and the closed cross-section can effectively prevent corrosion. They are mainly used in the following scenarios:
1. High-rise buildings: They are important vertical load-bearing components in high-rise building structures, and can withstand huge vertical and horizontal loads, such as wind and earthquake forces.
2. Large public buildings: Such as airport terminals, gymnasiums, exhibition halls, etc. These buildings have extremely high requirements for structural stability and safety, and box-type columns can provide reliable support.
3. Special structures: In some structures with special requirements, such as explosion-proof structures and nuclear power plants, the closed cross-section and high-strength characteristics of box-type columns make them an ideal choice.
3. Lattice columns
Lattice columns are composed of limbs and tie materials, with high stiffness and stability, and are suitable for the following scenarios:
1. Transmission towers: They are the main structural form of transmission line towers, and can withstand lateral loads such as the tension of wires and wind.
2. Large billboards: They provide stable support for large billboards to resist the effects of wind and other external forces.
3. Temporary support structure: During the construction process, it can be used as a temporary support column to support construction loads such as formwork and scaffolding.
4. Cross column
The cross column has a unique cross-sectional shape and can provide good bending and torsion resistance. It is mainly used in the following scenarios:
1. Complex building structure: In some buildings with complex shapes and special forces, such as special-shaped buildings and large sculpture-style buildings, the cross column can meet special structural requirements.
2. Large-span spatial structure: In large-span spatial structures such as airport waiting halls and high-speed rail stations, the cross column can be used as an important supporting component to form a stable structural system with other components.
3. Special industrial buildings: In some industrial buildings with special requirements for spatial layout and structural form, the cross column also has a certain application. First, the welded H-shaped steel, box column, lattice column and cross column are analyzed respectively. For welded H-shaped steel, considering its strong bending resistance and other characteristics, it is associated with scenes such as industrial plants, multi-story building frames and bridge projects. Box columns are suitable for high-rise buildings, large public buildings and special structures due to their good compressive properties. Lattice columns are composed of limbs and tie materials with high stiffness and stability, and are suitable for transmission towers, large billboards and temporary support structures. Cross columns are used in complex building structures, large-span spatial structures and special industrial buildings due to their unique cross-sections and properties.